Dogs, like people, will also have some diseases, such as mammary tumors. Of course, dog mammary tumors are also classified as benign or malignant, and the symptoms are also different. So how should you tell whether dog mammary tumors are benign?
1. Symptoms of dog mammary gland tumors
Dog mammary gland tumors mostly occur in old female dogs that have not been neutered. Upon inspection, you can see clearly defined raised lumps in the mammary gland area with different shapes, sizes, colors, and textures. Palpation reveals that the area is hard and the local skin temperature is elevated. At the same time, the dog will also be accompanied by symptoms such as depression, loss of appetite, and severe weight loss. Usually, the diagnosis can be confirmed by going to a pet hospital for B-ultrasound or X-ray.
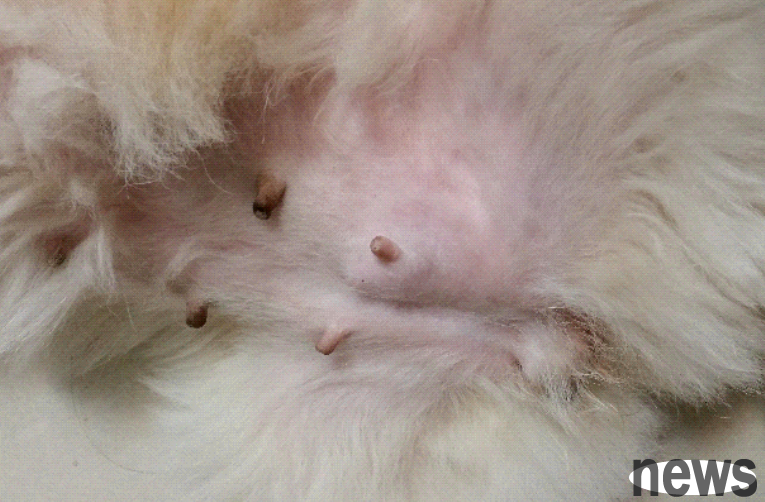
2. How to distinguish between benign and malignant breast tumors in dogs
Generally speaking, the characteristics of malignant breast tumors are mainly common in the last pair of mammary glands. Single or multiple masses can be seen in them. The masses are sometimes large and mobile. Inflammatory breast cancer may cause diffuse swelling of the breast, strong invasiveness, unclear boundaries, rapid growth, and abundant blood vessels. At the same time, malignant breast tumors may cause tumor metastasis.
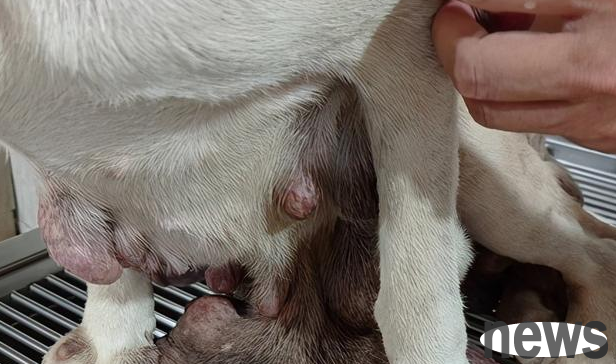
3. What to do about dog breast tumors
If a dog has a breast tumor, it is recommended to take the dog to the pet hospital for examination to determine whether it is a malignant tumor or a benign tumor and the size of the tumor. If it is a benign tumor and the dog is not very old, you can contact the hospital directly for surgical removal. However, if the dog is older and there are certain risks in anesthesia, you can communicate with the doctor at this time and carry out conservative drug treatment. If it is a malignant tumor, surgical removal is not recommended as it may still grow after removal.
